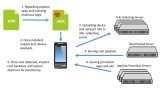
Checkpoint researchers identified a mobile malware named Copycat found infected with more than 14 million Android devices worldwide. The infected devices are found to perform ad fraud and has helped hackers make more than $1.5 million in the past 60 days. Once the malware is infected, it tries to root the device allowing the bad guys to gain full control of the device.
 CopyCat has the ability to replicate referrer id of its own. (Referrer id is used to track ads from google ads or bing ads). This means any ad revenue generated is sent to the hackers instead of the original intended recipient. The malware uses 5 different exploits which includes CVE-2013-6282, CVE-2015-3636 and CVE-2014-3153 infected devices running Android 5.0 and earlier.
CopyCat has the ability to replicate referrer id of its own. (Referrer id is used to track ads from google ads or bing ads). This means any ad revenue generated is sent to the hackers instead of the original intended recipient. The malware uses 5 different exploits which includes CVE-2013-6282, CVE-2015-3636 and CVE-2014-3153 infected devices running Android 5.0 and earlier.
280,000 of infected devices are from US, 381,000 devices are from Canada and the rest belong to the users from India, Indonesia, Myanmar & Pakistan. If the victim belongs to China, the app would not perform any activity. Hence Checkpoint researchers believe that the cybercriminals are Chinese and trying to avoid any possible legal troubles. Although there is no direct evidence of who is behind the attack.
Adding to that the researchers also have found evidence of several connections between CopyCat and the Chinese ad network MobiSummer. It also has been found that the malware and the ad company originate from the same server and the malware has been found to have been signed by MobiSummer, a Chinese ad company.
Google has been tracking this malware and has necessary measures to block CopyCat with Play Protect. However not all the Android devices are updated nor even possible to update and many fall victim due to phishing or by installing third party apps after rooting resulting in the same. However there is no evidence that this malware has been distributed by Google Play store.